Economics: Selected Topics in Overview
David Nollmeyer
A macro concept of investment and political economy is the multiplier effect.
This variable is the rate of consumption; currently near 18% per person, 18% per
dollar on average for the population.
In the taxing and redistribution of
income the government taxes the public taking money out of the economy shrinking
the money supply usually under some circumstance (budget needs). This will
increase the demand for money
strengthening currency. Money held in the federal reserve does not earn
interest.
According to moral assumption, public policy is devised, a budget
is crafted
to redistribute the taxes or money, the government paying itself and directing
the funds to various programs and outlays. This is subsidization.
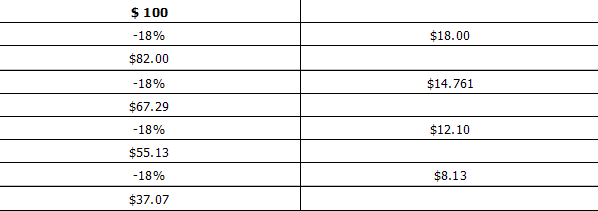
We shall use for simplificationís purpose $100 dollars to explain the multiplier
effect. The government will
introduce $100 dollars into a small program. A small table reads likewise:
Multiplier Table

In total 23 transactions subtracting 18.00% successively would leave $.85 cents
for this economy. Theoretically this could go on to infinity. The payment for
the service could be welfare, medication, or an arms supplier. The circulation
of the monies may move through various sectors by purchases by the
beneficiaries. Purchases may include hospital care, medicine, supplies, food,
metal, electronics, and labor until the whole 100% of the amount is spent.
The case being thus, the government
arguing to fulfill the constitution by legislation and funding the activity of
the political economy taxes and redistributes funds. By targeting sectors the
government stimulates sectors for growth.
Each person and contractor is taxed
the minimum around 30 to 35 percent. The taxes from each party and the movement
of monies should return the $100 dollars to the government in the final period
of taxation. This multiplier at 30% tax yields $105.24. This is a $5.24 net
return to the tax reserves.
This is known as the multiplier
factor. Conversely one could argue that the best multiplier is achieved by
living funds in the private sector. This assumption has been recently paired
with the flat tax model.
Variations could be extended over a
small fiscal period. The case being that the taxation should return the monies
used less a moral necessity or disaster, epidemic, or a military engagement.
Supply-side laizze faire thinking
argues that the government is an unnecessary inefficient consumer of wealth;
rewarding itself handsomely and thus producing less than capital would by
eliminating taxes and keeping capital unfettered.
Theorists of this nature argue the
greater multiplier, hence economy, expansion is created under the assumptions of
the private sector thus creating greater prosperity, employment, and economic
efficiency.
Much concern is now at hand worldwide
over the role of government; how policy movements should be implemented through
taxation and bonds. Socialists and communists radicals would like to see
government do more than classical thinkers arguing that the government is less
exploitive and fairer.
In a balance sheet there is a simple argument found that is also akin to budget
projections of every sort. This is planned investment equals planned savings.
We will use $1,000,000 for a hypothetical bank and its balance sheet.
The balance sheet is divided down the
center, planned investment to the left and planned savings to the right. Both
sides of the statements must balance, be equal.
Federal banking regulations currently state that 25% of assets must be held in
the federal reserve and 25% in securities to guarantee solvency.
From the initial charter of backers and primary lenders, deposits on 4-1 06 are
$1,000,000. This sum is entered in planned savings and then planned investments.
On 4-2 $250,000 is transferred planned savings to federal reserve. A loan is
made in PI from PS. Two investments are recorded in PI and then PS. Banks prefer
short term bonds to take advantage of interest rates. The bank must maintain 50%
percent of all assets in the federal reserves and securities that are not used
in loans and other banking operations (regulations).
Activity is ceased for 4-2, itemized
and the total carried over to 4-3.
The bank has $1,000,000 of which
500,000 may be used in lending. On 4-3 $500,000 in loans have been secured. The
bank has invested in PI $500,000 and now has $500,000 in PS. At the close of the
4-3 there I in PI $1,500,000 and in PS $1,500,000.
The bank now has $1,500,000 in paper
money or book money of which the bank managers and loan officers are responsible
for.
Balance Sheet
A most important consideration are the analysis of balance sheets in macro
political economics is the position of capital investment in the PI column. As
PS is converted into a capital investment of purchases of generators, tractors
something tangible facilitating the real structural productions of outputs
namely capital goods, GDP or Goss
Dependent Production, the economy will expand.
Aggregates of currency are known as
such:
M-1 Liquid - Simple investment, savings, money in circulation
M-2 Securities - less liquid - mortgages and bonds
M-3 Not liquid - federal reserve
The critical position of capital and capital goods and resources are shrewdly
targeted to create economy. When the capital position of currency
is favorable due to the addition and subtraction of these aggregates, the market
expands or on the contrary enters a depression. The movements of M-1 are good
for purchasing power. M-2 and M-3 may be correct for investment and savings
anchoring the currency.
Persons are sometimes requested to
break savings to supply money to the market to avoid the government intervening
by selling bonds which will introduce new printed money for the interest
payments. This is usually inflationary and the currency will devalue as the
supply of money expands.
This type of economy is sensitive to
capital and the financing of investments in addition to the needs of the capital
position. These are the capital investments to satisfy the needs of a demand
curve (fulfilling supply). This is the crux of market economics.
An entrepreneur analyzes all
aggregates, non proportional outputs of economy domestically and worldwide. A
rate of exchange has been enfranchised to one in political economy. One analyses
the differences in the rate of exchange, interest rates (rents) that exist
between goods and services. A calculation is made regarding the multiplier
effect, hence the marginal revenue and marginal cost of all the aggregates of
the economic assumption of the investment considered. The entrepreneur chooses
the best production, investment in a firm or product existing or potentially, to
fully make the most efficient use of natural resources and capital to complete
economic activity.
All assumptions are first carefully
deduced and calculated from the most complete morality or system of moral
assumptions towards the completion of the economic enterprise.
The federal reserve is also
predicated on a similar schema. The first bank, the national bank, the federal
reserve requires a minimum of 25% of currency in reserve to print new money.
The new currency is printed by the
treasury to facilitate the interest payment on bonds. Extra bond sales can be
seen as a deviant manner of printing bad money or devaluating the currency.
The management of currency through
open market operations should permit currency to re-circulate through the
economy encouraging the necessary growth of banking and private individuals.
Primary bankers and other
institutions shall have to deposit money in the federal reserve system to
maintain solvency strengthening their position as well or be attracted to bond
sales in a genuine manner in evidence of a healthy government.
Long term general equilibrium is an
analytical tool of a fully developed economy. It is used to gauge needs of whole
and individuals in policy creation. There are those that argue this analysis as
left of center. Market analysisís are more concerned with the multiplier effect.
There is a relationship but the two concepts have more distinct uses.
Long term general equilibrium is
derived after short term equilibrium.
When the least advanced individual in
the economic strata is satisfied and does not wish to enter and exercise oneís
economic assumptions, is genuinely happy as well as all upper and inclusively of
the most advanced public and private members of the economic community, this
economy has achieved equilibrium.
A simple person, e.g. an unemployed
person, decides to work; to gather fruit for sale to increase oneís economic
standards. The individual is desiring o be upwardly mobile. There is a demand
exerted in the market. One enters into the workplace seeking employment, the
collected fruit is sold in the market. One is now a competitor. The market is
not in equilibrium. The market adjust to the competitorís presence.
The small businesspersons also are
endeavoring to increase their activity. Competition creates saturation. Weak
businesses fail. Imitation has occurred.
Eventually there are many businesses that are
hierachialized with very advanced
specialized work differentiation and management. There are many fully developed
sectors and a great variation of goods and services which are reflective of long
term equilibrium. The workers of the failed businesses are displaced.
These persons and the entrepreneurs
are monopolistic competitors. These shall argue economic assumptions until they
are reabsorbed into the economy or are satisfied.
This activity is inclusive of the upper strata of government and CEOs are all
100 % satisfied in the exercise of their economic assumptions. This is long term
equilibrium.
If this is not the case the market will readjust. Similarly it most be noted
that all members must be free to vocalize and move their will otherwise long
term general equilibrium will not occur.
Theorists have debated this issue.
Some argue that it could never occur. It is utopic; analytical tool to measure
the aggregates of economy, movement of sectors and individuals towards a fully
developed economy. This model has a linkage in state planning and social theory.
Generally speaking long term general equilibrium is an inductive model that is a
target to shoot at.
In conclusion of monopolistic
competition in pure and perfect markets argues that the description of a more
efficient economic engine for accumulating wealth in an economy, is that all
economy bears some relationship to propriety and property and is therefore
monopolistic. These positions are either one of state or private monopoly.
The adaptation of these principles are suitable by spiritual, moral, and
ideological reasons for first assumptions which must be again tested to prove
validity.
A brief note shall conclude with a
small picture of political economy. This is the classicist position.
Classicist argue the free trade position that market economics create greater
wealth, stability, and allows for greater freedom to participate. Hard work will
pay off in the long run. Classicists would like to see this position universally
applied permitting for the same entrance to every market (perfect market)
worldwide with legal rights of private property and investment (intellectual
property). This position is antinationalization. Economy is more efficient if
property is kept in private hands. Bankers, the International Monetary Fund (IMF),
and the World Bank share in the classicist position. These actors are concerned
with the printing of money, balance of payments, the paying off of debt
and interest, and a positive sum line.
These arguments are dominated by
United States and Japanese baking institutions with European interests. These
institutions control the capitalization available to nationalities.
The United States may be seen as
integral to the IMF and World Bank. These agencies lend in combination from
different countries agencies through the United Nations with other credits as
grain. The United States is a highly advanced economic interest exerting a great
amount of pressure for the protection of patents and technology transfers. This
reflects a position of the North Alignment.
Radicals are advocates of the South
Alignment. This position argues that the classicists and bankers form a club or
conspiracy against emergent economies. The South demonstrates a distrust in the
Northís interest in exploitation of natural resources from these nation states
resulting in capital flight.
Radicals at times argue the protection of sectors or industry from competition.
Nationalization is acceptable to pool resources and limit competition. This is
known as economic nationalization.
Multinational corporations that have
a headquarters in a foreign homeland tend to redistribute profits to these
nations. Trans- nationals where ownership is more diversified through stock
ownership in many nations is more desired than the concentration of capital
in New York, Tokyo, or Frankfurt.
Autarky is a possibility. This in a
simple form is functioning strictly from a domestic production and withdrawal
from international trading, It is similar to a war economy. At the minimum it is
the maintenance of the species life. Blockades appear to be futile as a country
would be able to isolate itself and outlive the sanctions. Ideology and moral
positions are also antecedent to voluntarily isolating a nation an economic
assumption for autarky.
South countries would like to see
technology transfers. Radical economies had its champion in Marx but has move
towards market socialism or socialization of the market. The two are somewhat
different with the former more market oriented, the latter the ends not
necessarily accepting the market as a primary structure for social justice.
Both positions argue a welfare state
balanced by private and nationalized industry.
Below are a few of the measures of
the orthodoxy of Marx in establishing the proletariat and the beginnings of
socialist and communist economy: command or state economies.
1. Abolition of
property in land and application of all rents of lands from private purposes.
2. A heavy
progressive graduated income tax.
3. Centralization
of credit in the hands of the state, by means of a national bank with capital
and exclusive monopoly.
4. Centralization
of the means of transportation and communication in the hands of the state.
5. Free education
for all children. Public Schools. Abolition of child factory labor.
The collectivization of production in
the whole nation-state is organized as an extension of the proletariat. This is
a universal argument and revolutionary. Pure communism is not exactly pure, and
will never occur. Divergence of philosophy has occurred.
Anarchistic thinking with more
individual commands has emerged. This position rejects macro-authority. New Left
thinking includes positions on social orientation, mobility, environment, the
welfare state, and market economics. Euro Communism stresses election and
communism. In Africa this formula stresses Islam.
Returning to economics, nations are
concerned with balance of payments of which are: 1. Positive sum 2. Zero sum 3.
Negative sum.
In this schema accounting for 100% of
economic activity (which is derived from the gold points), if a nation is
positive sum another is negative sum. All nations have a balance of trade
bilaterally and multilaterally that is accounted for. Classicists posit a
positive sum position as favorable. To mercantilist a zero-sum outcome is
acceptable. Radicals posit a zero-sum model although this is more idealistic
than realistic.
In the real world there are nation
states that are less than self-sufficient. They are wise to attempt to locate
aid outside of their country to develop economic justice. There is an
interdependence of economies and this in their favor. It can be noted in a
general sense the ability of a country to export product is essential to its
well being. The United States, the worlds largest economy depends on exports to
secure one out of three jobs. There is less wealth in the United States to
purchase all of its production. Protectionism creates unemployment. The closed
command systems are failing under competition.
Classical economics predicates the
efficiency of market forces. It is to be seen if the maximum gun can
simultaneously achieve the freedom that is argued as integral to the economic
assumptions necessary to fulfill its theory. Economics of either the left or
right will not achieve social justice. This activity is regulated to morality
and spirituality.
The current argument in closing is GATT, the General Agreement on Trade and
Tariffs which has had at its objective the elimination of protectionist tariffs,
barriers, and subsidies which are detrimental to free trade and a free market.
GATT has failed. This supranational regime is the master plan for the European
Common Market (ECM) and the North American Free Trade Association (NAFTA). The
regional trading blocks based on similar thinking have been more successful than
a universal zone.
The trajectory of augmentation over
the long term is to help nation states devise and adapt a common business
practice. This augmentation is one of free trade with the radicals endeavoring
to redirect wealth to the social welfare state.
The current strategy is to incorporate the
Eastern European states in political economy.